When the compressional force applied under high confining pressure, rock
beds tend to yield folding. Fording result in shorting and thickening
of rock bed
Terminology
Anticline, Syncline, Limb, Axial plain, Axis of fold,Plunge of fold
Types of fold
Symmetrical fold - Two limbs dip in same angle but in opposite direction, axial plain is vertical and passing through crest and tough.

Asymmetrical fold- limbs dip in unequal angle in opposite direction. Axial plane need not necessarily pass through crest and tough, and it is inclined.

Overturned fold - asymmetrical fold with one lime turned past the vertical and both limbs dip in same direction.

Recumbent fold - folding is so intense that both limbs become almost horizontal and axial plain too in horizontal. lower limb gets overturned.

Isoclinal fold - folds with parallel limbs
1. Vertical Isoclinal fold
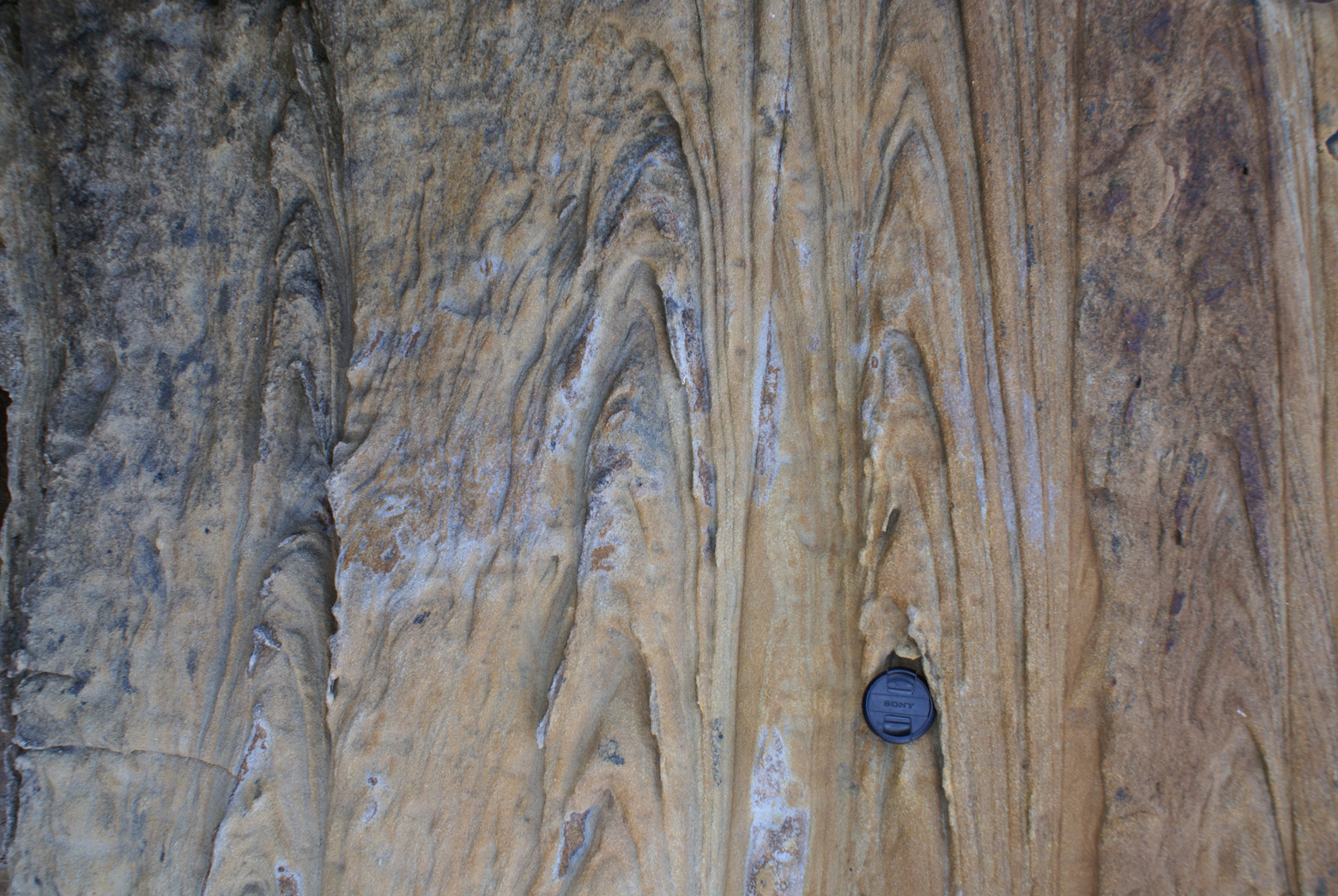

2. Inclined Isoclinal fold
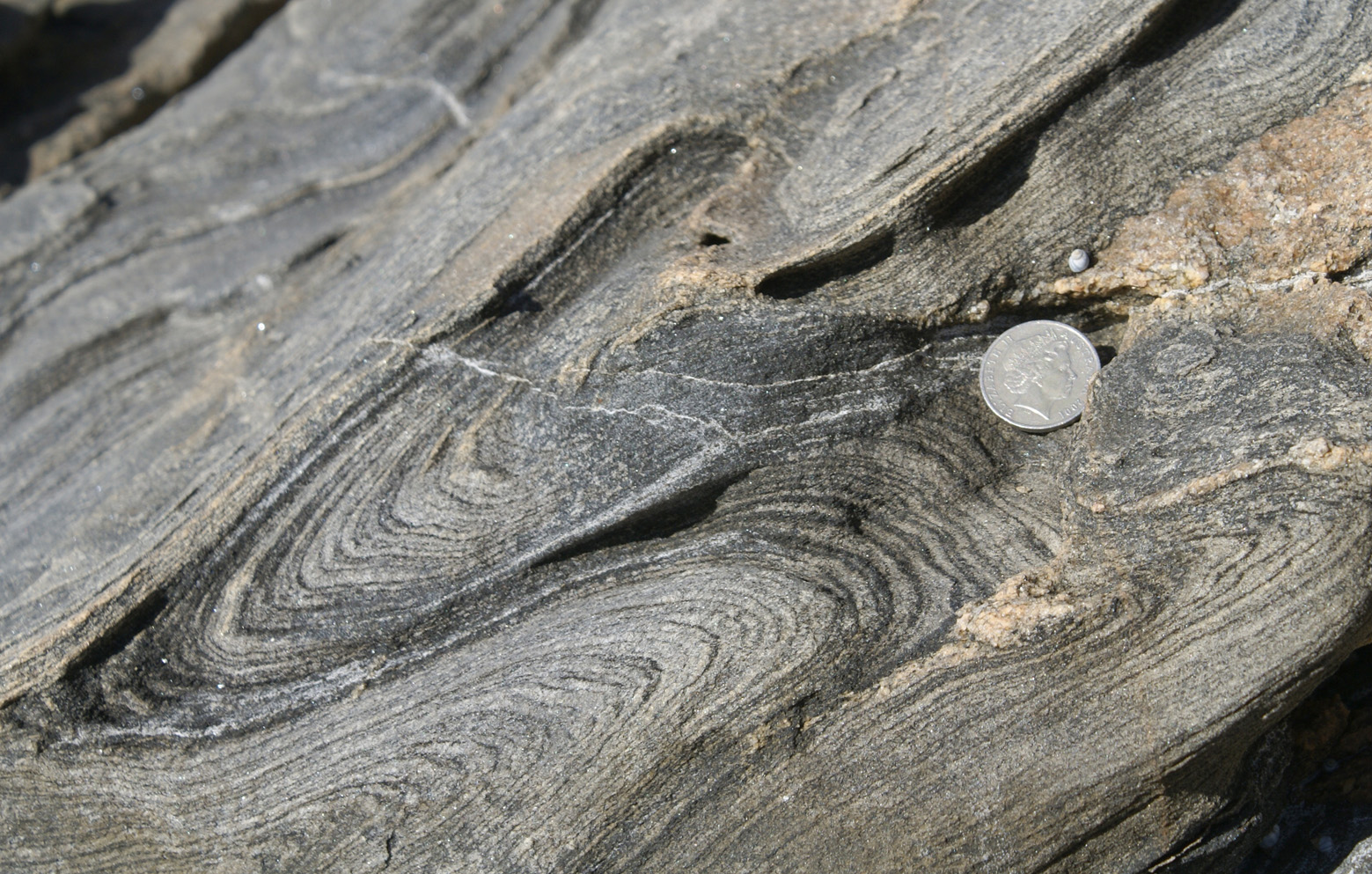

Nonplunging fold- syncline and anticline whose axis are horizontal
Terminology
Angle of plunge - the angle of inclination of axis from the horizontal
Direction of plunge - the direction in which the axis is inclined
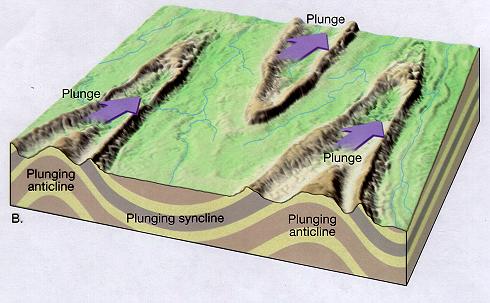
nose - indicate the direction of plunge. In anticline, plunge is directed towards nose and in syncline it is directed away from nose.
Plunging fold - if axis are inclined


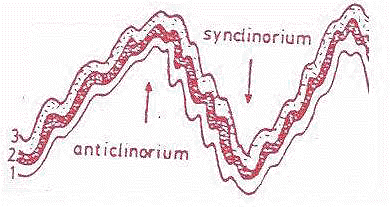
Anticlinorium - these are the complex large folds in the form of syncline and anticline with sub-fold on there limbs.
Open - limbs meet at bents at an obtuse angle and thickness remain unchanged.

Closed fold - folding is so tight that incompetent strata flow plastically towards crest and tough due to minimum stress. It cause thinning at the flank and thickening at crests.
Doom and Basin - when strata are subjected to folding in two direction at right angle, each anticline convert to doom and syncline to basin. Doom is up-fold where beds dip radially outward in all direction from centre and vise verse.

Fan fold - upright fold with both limbs overturned. The bed within the anticline are much compressed below while they open out above. Crest and tough are generally rounded.

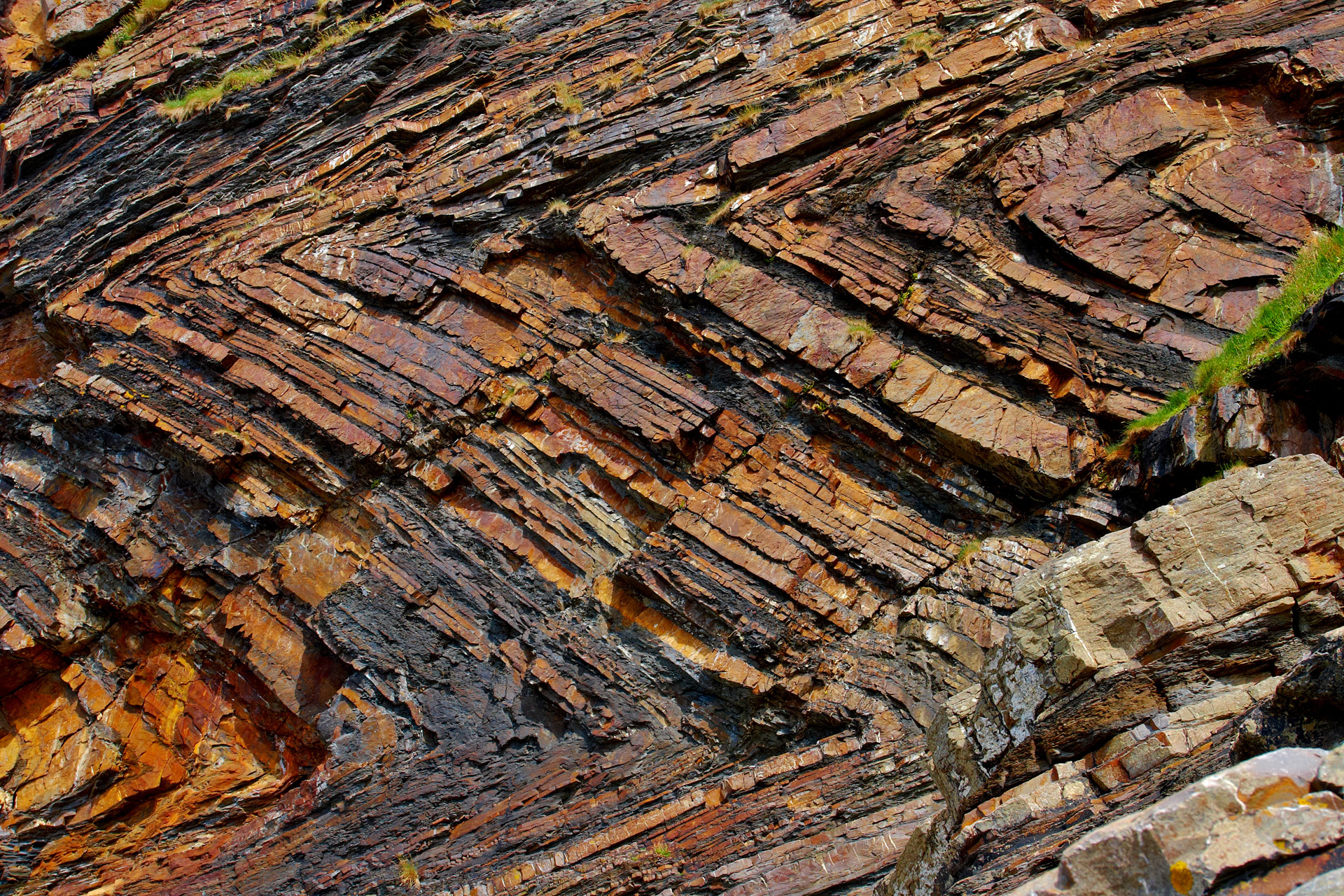
Chevron fold - fold with straight or nearly straight limbs, their crest and tough become sharp and angular.

Homocline - when bed dip with same angle and direction for few kilometer or more.
Monocline - local warping in horizontal strata. Rock beds lying at two level separated by steep inclined limbs. It is form by vertical movement and generally found fault below monocline.

Structural Terrace - local flattening in uniformly dipping bed.

Drag fold - minor fold developed within the incompetent bed during the process of major folding.
Terminology
Anticline, Syncline, Limb, Axial plain, Axis of fold,Plunge of fold
Types of fold
Symmetrical fold - Two limbs dip in same angle but in opposite direction, axial plain is vertical and passing through crest and tough.

Asymmetrical fold- limbs dip in unequal angle in opposite direction. Axial plane need not necessarily pass through crest and tough, and it is inclined.

Overturned fold - asymmetrical fold with one lime turned past the vertical and both limbs dip in same direction.
Recumbent fold - folding is so intense that both limbs become almost horizontal and axial plain too in horizontal. lower limb gets overturned.

Isoclinal fold - folds with parallel limbs
1. Vertical Isoclinal fold
2. Inclined Isoclinal fold
Nonplunging fold- syncline and anticline whose axis are horizontal
Terminology
Angle of plunge - the angle of inclination of axis from the horizontal
Direction of plunge - the direction in which the axis is inclined
nose - indicate the direction of plunge. In anticline, plunge is directed towards nose and in syncline it is directed away from nose.
Plunging fold - if axis are inclined



Outcrop of plunge
Anticlinorium - these are the complex large folds in the form of syncline and anticline with sub-fold on there limbs.

Open - limbs meet at bents at an obtuse angle and thickness remain unchanged.
Closed fold - folding is so tight that incompetent strata flow plastically towards crest and tough due to minimum stress. It cause thinning at the flank and thickening at crests.
Doom and Basin - when strata are subjected to folding in two direction at right angle, each anticline convert to doom and syncline to basin. Doom is up-fold where beds dip radially outward in all direction from centre and vise verse.

Fan fold - upright fold with both limbs overturned. The bed within the anticline are much compressed below while they open out above. Crest and tough are generally rounded.
Chevron fold - fold with straight or nearly straight limbs, their crest and tough become sharp and angular.

Homocline - when bed dip with same angle and direction for few kilometer or more.
Monocline - local warping in horizontal strata. Rock beds lying at two level separated by steep inclined limbs. It is form by vertical movement and generally found fault below monocline.

Structural Terrace - local flattening in uniformly dipping bed.
Drag fold - minor fold developed within the incompetent bed during the process of major folding.
No comments:
Post a Comment